Demystifying buffer() operator in Kotlin flows
I have been trying to understand flows and operators. During this time I cam to know about an operator called buffer()
Read More





Published on Dec 10, 2017 by Vipin Kuma on Android Architecture patterns
So I have been programming android for like 2 and a half years. I mostly used to program in Java with MVP pattern. Recently I saw google releasing their architecture components library. All these components work very well with MVVM. So I decided to learn this pattern. So in this article I’ll be sharing what I learnt about MVC , MVP and MVVM pattern from various resources. These are not my personal views. Everything is from the community.
Before starting with MVC, MVP or MVVM. Let’s understand why do we need an architecture pattern.
I’m going to put it in this way. Over 2 years of writing code for Android, I have realised that solving a problem or implementing a feature at that point of time is not enough. An android app goes through a lot of change cycles and features addition/removal. Incorporating these over a period of time creates a mess in your application if not designed properly with separation of concern. That is why we should use an architecture pattern.
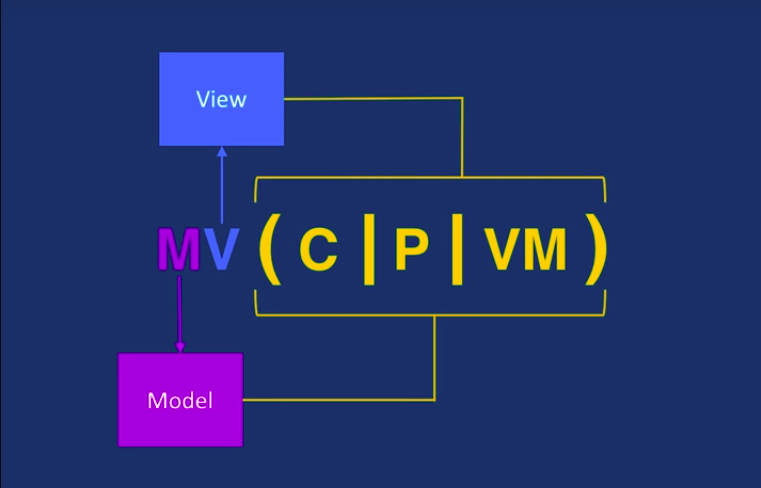
MVC, MVP and MVVM , they all have 2 elements in common M : the Model and V : the View. And the role of these 2 is pretty much the same throughout all these patterns.
[IMAGE HERE]
Its in charge of the business logic. So it talks to network layer and database and exposes the data to whoever needs it. It should be a completely independent component from android.
Anything responsible for displaying the data.
(C,P,VM) : C : the Controller, P : the Presenter and VM : the ViewModel are working with the model to get the data.
And the VIEW is working with the Controller(in MVC), the Presenter(in MVP) and the ViewModel(in MVVM). The way this interaction happens is pretty different in these patterns .
MVC : Model-View-Controller
[image here]
In MVC we have a View that talks with the Model and the Controller. And the Controller talks with View and the Model.
The Controller gets the user input then updates the Model. Once the Model is updated the Controller will tell the View to update. And then the View will get the latest data from the Model and update it.
MVC in Android
In Android our Activity serves as both View and Controller. Model is independent.
[image here]
So the whole point of an architecture is to split the responsibilities and make the code more testable. But the problem is, this architecture is not testable. The Model is testable. But the the View and Model are not testable.
So how to solve this, to split the responsibilities and make it more testable, we need to remove the Controller from the activity. And have the Activity(View) accept the user input. Once the View accepts user input, it should inform the Controller and the Controller should update the Model. Then Controller should tell the View to update itself. Then the View should fetch latest data from the Model.
[image here]
But there are still problems. First : Separation of Responsibilities : Here View and Controller both can access Model. If this is the case why are we using Controller. Second : Testability : View and Model have direct references to each other which makes it hard to test.
MVP : Model-View-Presenter
In MVP we have a View and a Presenter. Every View has a Presenter and every Presenter has a View(1 to 1 relationship). They interact with each other through interfaces. The View has a reference to interface implemented by the Controller and similarly the Controller has a reference to interface implemented by View.
[image here]
View notifies the Presenter about user actions. The Presenter performs actions based on View’s requirements like updating the Model. And finally updating the View. There are few important things to understand about this pattern, which are:
Clearly there is Separation of Responsibilities. And since the View and the Presenter** refer each other through interfaces, the code is easily testable.
If you want to deep dive in MVP implementation, I have a repository at github. Go and check it out :
[repository link here]
So lets look at this architecture from a different perspective. Let us look at this architecture from Event-Based point of view. Then we can say that Presenter would be the one that produces data and the View would be the one that consumes data. So if the Presenter is the producer, why should the producer know about the consumer. The producer should not care who consumes the data. The producer should provide streams of data, and whoever wants it should subscribe to it. So this leads to another pattern which is MVVM.
MVVM : Model-View-ViewModel
The main purpose of this architecture pattern is to simplify the Event-Based implementation of the user interface. In MVVM, we have ViewModel that gets the data from the Model, it applies the UI logic and it exposes it to whoever needs it, it can be the View, it can be the tests or any other classes. And the View would just subscribe to the ViewModel.
[image here]
MVVM reduces the boilerplate code compared to MVP. MVVM with Rxjava2 is a perfect match to create Event-Based UI in an Android App.
If you want to deep dive in MVVM implementation, look into this repository:
[repository link here]
MVC vs MVP vs MVVM
MVP and MVVM provide separation of responsibility and testability. But MVC vs MVP vs MVVM , which one should you use? It actually does not matter. Just ask these 3 questions :
Are your Android classes logic free?
Can you unit test everything?
Do your classes do one thing and one thing only?
If you can answer with YES, to all these 3 questions, it means you have a Robust, Stable, Testable, Modular, Easy to Extend application that you wanted.
Thank You.

I have been trying to understand flows and operators. During this time I cam to know about an operator called buffer()
Read More
So I have been programming android for like 2 and a half years. I mostly used to program in Java with MVP pattern. Recently I saw google releasing their architecture...
Read More